Some appliances perform vital functions, and people are not aware of them just because they are small or not within the eye’s grasp most of the time. These mechanical parts are used daily, and a minor fault could render a giant machine useless. An example of this is the ballall valve.
Ball valves are used in every industry, from healthcare to mining, food processing, oil and gas, and even homes.
What is a Ball Valve?

A ball valve is a mechanical flow control device that is used to modulate and direct the flow of liquid through it. This shut-off ball valve serves as a guide to handling different substances like gas, petrol, and other pressure liquids flow. The ball valve uses a perforated, hollow, and pivoting ball to achieve this.
This valve consists of a spherical obturator with a cylindrical hole as wide as a pipe, valve handle, and ball with a hole drilled into it. It is put to work by rotating the ball (using the handle) 90⁰ around its axis; this either lets the substance go through or blocks its movement.
After the handle is rotated, the valve gets to a closed position, and the solid side of the ball effectively creates a seal and obstruction, keeping the contents of the substance trapped.
Ball valves are solid, durable, and easy to repair. They are an excellent choice for industrial and personal shut-off applications. Ball valves are used in various hydrocarbon process applications; they are capable of throttling gasses and vapor.
Ball valve symbol
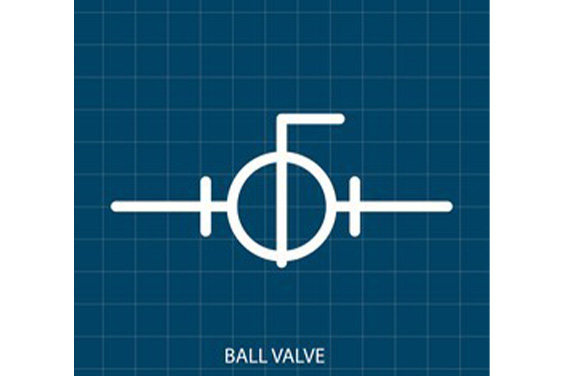
Ball valve symbols can be classified into two – the two-way symbol and the three-four-way symbol.
Two Way Symbol
The two-way symbol is demonstrated by two equilateral triangles that point at each other, and there is a ball at the center. The triangles are in the shape of arrowheads bumping face first against each other.
The Three-Four Way Symbol
To represent ball valves with multiple ports, additional symbols were added. The T-port and L-port valves are represented with lines within the ball symbol. They are symbolized in 6 different variations with a small arrow showing the flow path beside the symbol.
Common Types Of Ball Valves
Ball valves come in different specifications.
Standard Port Ball Valve

The standard Port Ball Valve flow is usually smaller than the valve’s pipe size. For a pipe valve diameter of up to size 12″ NB, the bore diameter is usually one size less, 2 and 3 less for a pipe diameter of valve sizes 14″ NB to 24″ NB, and for sizes above 24″ NB, respectively.
What this means for the user is that it will slightly limit or restrict the pipe content’s flow even when opened to the last.
This type of ball valve is less expensive compared to most other common types of ball types. They are durable and have a higher pressure drop.
Standard Port Ball Valve is ideal for use with a high flow coefficient.
Full Port Ball Valve

What is a complete port ball valve?
Also known as the Full Bore valve, full Port ball valves have an oversized ball and a borehole with the exact fitting of the pipe that leads to the valve.
The entire port or full bore valve does not cause frictional loss, and allows pigging, thereby making it very easy to clean mechanically.
This type of ball valve is more expensive due partly to its higher weight than the standard ball valves. Full port valves are used in steady and high flow coefficient situations; it is the best valve for flow control.
V Port Ball Valve

The V Port ball valve comes either as a V-shaped seat or ball. This allows the opening and closing of the orifice to be much better control-wise. The flow characteristics of V Port ball valves are just about linear.
The V ball control valve does not have a borehole. It is a floating ball that gets compressed whenever the valve opens, and when it is closed, the ball goes back to size, blocking the valve’s in and out ports perfectly, giving it a tighter seal.
For the reason of high fluid velocity, which might damage a standard valve quickly, good industrial valve manufacturers make sure the design is given a more robust construction.
Multi Port Ball Valve

The multi-port ball valve is a 4 or three way ball valve type with multiple connectors that allow the flow of substances to be diverted into as many directions as needed.
There is an L to T-shaped hole in the middle of the three or four-way ball valve. The L valve allows the center port to connect to either side of the ports or even disconnect the three, but it can not cause a connection between the two side ports.T valves, on the other hand, can connect any pair of ports at all or even all three.
The four-way ball valve comes with two L-shaped ports that can not connect to each other. They are sometimes called “x ports.”
True Union Ball Valve
Trunnion mounted ball valves have two shafts at the sides of the ball facing each other, which enables the valve to support the segmented ball, thereby reducing the friction that occurs between the various parts of the Trunnion ball valve. A pin is used to stop the ball’s movements and secure it in place.
Trunnion ball valves can be applied in systems that have high velocity and pressure (about 600 psi upwards) since it is capable of withstanding more pressure than the standard ball valve.
This type of ball valve has double unions, which can be sealed at either end. This allows them to be completely removed from a piping system for repair or replacement.
Manually Operated Ball Valve

The manually operated ball valve is a common type of ball valve that can be manually controlled with the aid of a handle that is placed outside of the pipe.
Due to its simple and minimalistic design, manually operated ball valves are easy to use. It takes only a quarter turn to open and close the valve.
However, because manually operated ball valves can be closed quickly, it poses the risk of water hammer
Motorized Ball Valve

Motorized ball valves are the type of ball valves that are primarily used in big industrial plants and automated factories. They are electric-powered ball valves.
With motorized Ball valves, opening and closing valves are done by an electronically powered motor that is placed over the valve.
Sanitary Ball Valve

These types of ball valves come in different sizes and configurations manually, mechanical, or electric powered.
Sanitary ball valves are primarily used in the food, beverage, health, and pharmaceutical manufacturing industries. These valves are basically for applications in cases where sanitization is required.
Sanitary ball valves have smooth and polished surfaces, which helps to prevent the build-up of debris.
What Are Ball Valve Parts?
Below are six crucial parts that can be found in every ball valve:
- The body
This is the central part of the entire device and contains all of the internal components. Usually, a valve’s body is made of metal, metal with ceramic or plastic.
- Ball
The main characteristic that differentiates ball valves from other valve types is a ball with a center hole or bore. It is through this center hole that the media flows. This hole connects the inlet to the outlet through one axis. The ball is either free-floating or Trunnion mounted.
- Seats
The seats are discs placed in between the body and the ball. They support the ball and provide a seal between it and the body. The ball valve seats distribute the seating stress uniformly and serve as a seal (usually a polymer or elastomer) that keeps the fluid locked inside.
- Stem
It is the stem in a ball valve that connects the rotary ball to an external control system. In a manually operated ball valve, for example, it is the stem that is connected to a lever or handle.
- Power Source
For the stem of the ball valve to be able to rotate, a manual or actuated power source is required to provide energy to it.
Automatic Actuated energy uses an electric, hydraulic or pneumatic power source, while manual actuators use handles and levers, which an operator will have to control.
- Packing
The packing is a seal around the stem that prevents the substance from escaping.
- Bonnet
The bonnet is visible in the opening of the body; it is used to cover this opening in the ball valve. The bonnet also serves as a pressure boundary. It accommodates the ball and stem assembly with its cap fastened tight to the body.
What Does A Ball Valve Do
What is a ball valve used for? Well, ball valves have numerous functions and this makes them really popular amongst manufacturers. They are the most commonly used mechanical device for not only industrial but household applications as well.
The first and primary ball valve function is to create isolation. Ball valve is used for making a turn on/turn off action. Ball valve types are incredible for applications where an on/off action is required. Whether manual or electronically operated, ball valves are able to turn actions on and turn them off after.
The ball valve handle serves as an indicator of the valve’s on/off status. If the handle is parallel to the valve, this means it is open, but if the handle is perpendicular, this means the valve is closed.
Another thing a ball valve does is reduce or restrict the flow of the medium. Flow reduction is a secondary function of ball valves. The rotary ball of the ball valve is used for controlling the flow of gasses or fluids. When the bore in the ball is in line with the direction of the flow, substances can pass through freely. However, when the ball is turned 90 degrees, there is a complete halt to flow.
What Are Ball Valve Applications?
One reason for the popularity of the ball valve over all other kinds of valves is its versatility. Ball valves can be utilized across a wide range of applications. They are good with both liquids and gasses. Some significant applications of ball valves include:
Oil and Gas

The oil and gas industry could easily be the most significant users of the ball valve as they deal entirely in liquid and gaseous substances. Ball valves are used as isolation valves for thermal cracking units. It is also used to measure and meter the gas distribution, amongst multiple other use cases.
Pharmaceuticals

Like oil and gas, another industry that uses and requires ball valves the most is a pharmaceutical company. It is in this application that sanitary ball valve types are used a lot.
Petrochemical

Ball valves in the petrochemical industry are used to handle highly viscous fluids, for emission control, etc.
Other practical applications of Ball valves can be found in the following:
- Water Supply Industry
- Food Production
- Vehicle Wash Systems
- Outdoor hoses
- Irrigation Systems
- Automotive Industry
How Does A Ball Valve Work?
The ball valve works rotationally. When the stem transfers motion to the ball connected, the ball starts to rotate. The rotation of this ball then helps the bore to either open or close, which in turn causes the fluid to start or stop flowing. The actuator has to rotate out 90 degrees clockwise for the fluid to start flowing; to stop it, it has to rotate back 90 degrees again, turning the stem in an anticlockwise direction.
To get into more detail, for a manually operated ball valve, when the opening of the ball matches the inlet and outlet ports, the flow of substance continues uninterruptedly through the valve. It will undergo a minimal pressure drop if it is a complete port ball valve being used. The pressure drop will increase if it is a standard port ball valve.
If a substance is currently flowing through the pipes, then the operator must be placed parallel to the pipeline. This also indicates that the ball’s flow passages are in line with the body’s flow passage, hence the media flow. To stop the flow, however, the hand operator will need to be turned to the closed position. When this is done, the opening of the body starts to move perpendicular to the flow stream, and the edges of the port begin to rotate through the seat.
Once the handle is at the fully-closed position, the hole is now positioned perpendicular to the flow stream, thereby blocking and preventing anything from going past the ball.
To achieve a throttling ball valve flow, the ball should be in a partially open and partially close position. This position should, however, not be maintained under high pressure conditions for a very long time because the balls could become permanently locked in that position.
Ball Valve Installation And Maintenance

Before installation commences, all welding works must have been completed, and the flanges cooled down to ambient temperature. It can be installed appropriately by following these ball valve installation instructions:
- Check the material of the entire valve, the body, seat, and the ball to make sure there are no possible defects that could have been caused by storage or in the process of shipping.
- Check the valve’s pressure rating in comparison with the ball valve application requirement
- Make sure the ball valve’s flange (ANSI 150, NPT, socket weld ANSI), thread (NPT, BSP, socket weld ANSI), and the solvent weld (BLP schedule 40) meet the application requirements.
- Clean the flange’s surface, so it is free from debris when it comes in contact with the ball valve.
- The valve must be supported where necessary so that the load on the piping is reduced, especially when working with bigger valves.
- Install a pipe union. This will allow the valve to be removable for maintenance; it is indispensable when working with metal pipework for two and 3-way valves (BVS, BVF8 & BLS3)
- Now ensure that bolts are well tightened on a flange valve one after another. Apply pressure to form a seal between the flanges and valve.
- Once that is complete, put the valve to work severally to make sure there are no impingements. If this is done, the device is now ready for operation.
Maintenance
Proper ball valve maintenance culture will help increase their lifespan. To maintain:
- The valve should be cycled once every month if it is not active.
- Clean the valve using a towel to wipe off dirt, oil, or dust regularly. Do not use cleaning agents that will react negatively with the valve’s material.
- Lubricate regularly using water-insoluble, synthetic, or oil-based lubricants.
- A routine inspection should be carried out at intervals by a trained inspection officer.
Ball valve packing
Valve packing is the seal required in valves to allow motion of the stem from an actuator. Packing makes sure that the process fluid is sealed and there are no leaks between the moving stem and the valve’s body.
The commonly used type of packing is the Chevron V-ring type packing. Ball valve packing stops the flowing media from leaving the body of the valve through the stem opening Inside the bonnet.
The packing material takes the form of multiple concentric rings, which are usually stacked on top of each other; the stem is then inserted through this packing.
The packing flange forces these packing rings down from above to put a compressive force around the valve stem’s circumference.
This force is significant because that is what creates mechanical stress in the packing material, allowing it to seal tightly against the valve’s stem and the bonnet’s interior wall.
The two nuts used to maintain proper force on the packing should not be over-tightened as this could over-compress the packing material. If this happens, there will be excessive friction on the valve’s stem, which will cause the stem to wear over time and might lead to leakage.
What to consider before buying ball valves?
Before purchasing ball valves, several factors need to be put into consideration so as to get the perfect value for money. Some of the things that should be considered before buying ball valves include:
Material
Nobody wants to buy a product made with the wrong material, unsuitable for their case application, or even counterfeit materials. Ball valves are made with different materials, some of which are:
- PVC: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a type of plastic used especially in making industrial water valves. It is a durable, rugged, and rigid material. One main advantage of PVC ball valves is that they are less expensive than most other materials. PVC valves are corrosion resistant.
- Stainless Steel: it contains chromium in high quantity and some nickel too. Stainless steel is used in making different ball valve types be because of the many essential attributes it contains. It is famous for its durability and high corrosion resistance.
- Iron: This material is the most commonly used in oil and gas, water, and steam lines. This is because iron is capable of resisting a wide range of pressure and temperature
- CPVC: CPVC or chlorinated PVC contains almost all the features of PVC; the difference is that CPVC can withstand higher temperatures. It is suitable for ball valves that handle hot water.
- Bronze and Brass: this material is water and corrosion-resistant. It is popular because of its shiny surface, high durability, and toughness. Bronze and Brass ball valves are an ideal ball valve for high temperature applications.
- PP: Propylene monomer is also used for making Polypropylene Ball Valve (PP). It has the ability to resist acids and bases. This material is durable, flexible, lightweight, and rigid thermoplastic. Polypropylene Ball Valves are commonly used in the consumables industries like sugar, flour, etc., and other products like chemicals, fertilizers, and paper, among numerous lots.
Design
Ball valves come in different designs, as will be required by the specific purposes they were designed for. The user application determines the design that should be bought.
Popular ball valve designs are:
- Full Bore
- Reduced Bore
- V-shaped
- Vented
Ball Valve Standard
Before buying a ball valve, it must be certified standard by the relevant organizations.
They are:
- ANSI: the American National Standards Institute is an organization saddled with the responsibility of setting voluntary safety standards for manufacturers in the United States. Check for ANSI’s label on ball valves to confirm their safety.
- Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC): The Uniform Plumbing Code are set of codes and standards set by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) to ensure the safety of both plumbers and consumers alike. All the best types of plumbing valves have this.
- Underwriters Laboratories (UL): this global organization is responsible for testing mechanical parts, which includes ball valves, to ensure that they function correctly. The UL also devotes itself to promoting safe industrial practices in industries of all countries.
Ball Valve Sizes
Ball valves come in numerous varying sizes. Although some ball valves are made custom to fit specifications, there generally are standard sizes that are common in the ball valve market.
The sizes have their specific purpose, which they serve, a size for a function. When buying a ball valve, check for the size suitable for your application so as not to buy the wrong one. Some of the standard sizes you will find on the label are:
- 2-inch ball valve
- 1-inch ball valve
- ¾ ball valve
- ½ ball valve
- ⅜ ball valve
- ¼ ball valve
Working Pressure
The working pressure, as seen on the label as ratings, indicates the application type a ball valve is most suitable for.
Some of the pressure ratings you will find are:
- Pressure Nominal Classes (PN)- the PN Class number tells you the amount of pressure the ball valve is able to withstand. It is displayed on the item as bars, and each bar represents 14.5038 pounds of pressure.
- PSI Rating – PSI stands for pounds per square; it is commonly used in the United States as a measurement of pressure for equipment and instruments. PSI rating indicates the pressure of liquid or gas that a ball valve is capable of allowing its flow through the pipe.
- WSP Rating: WSP stands for Working steam pressure, which tells buyers the maximum pressure of steam that a ball valve can withstand at the highest temperature rating.
- CWP & WOG Ratings: CWP stands for Cold working pressure and WOG for Water, oil, and gas. CWP indicates a ball valve’s maximum pressure rating between the temperatures of -20° Fahrenheit to 100° Fahrenheit. CWP is commonly used with the valve’s pressure rating.
The WOG rating, however, has become old and is no longer used as often as it was before. This rating means that it is suitable for water, oil, and gaseous substances applications.
Conclusion
The ball valve is one of the most reliable in household and industrial applications. They are ideal for handling almost all forms of liquid and gaseous substances. Most ball valve applications exist because of the valve’s ability to tolerate high-volume, high-pressure, and high-temperature uses. It is highly durable and resistant to corrosion. Find reliable ball valve manufacturer could help you save money and cost. Feel free to contact us now.









